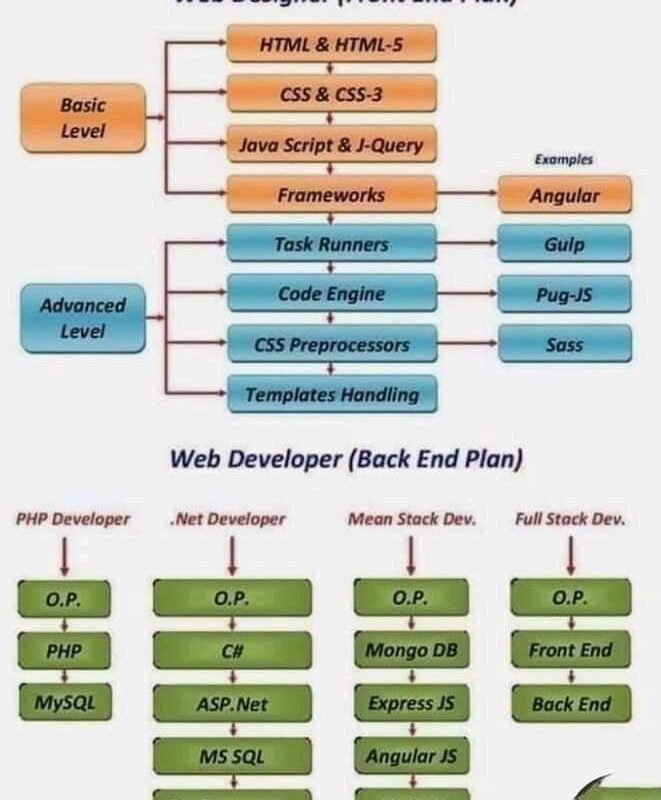
Embarking on the journey to become a full-stack developer can feel like navigating a complex maze. What exactly does it mean to be a full-stack developer, and where do you even begin? A full-stack developer is a versatile professional capable of handling both front-end and back-end development, essentially building all facets of a web application. Many aspiring developers find themselves overwhelmed by the sheer volume of technologies and skills required. They struggle to find a clear path, often jumping between tutorials without a cohesive understanding of how everything fits together. This article aims to offer a thorough full-stack developer roadmap specifically designed for beginners. We’ll break down the essential technologies, skills, and tools you need to learn, offering a structured approach to guide you from novice to proficient. This roadmap will cover front-end development (HTML, CSS, JavaScript, and popular frameworks), back-end development (Node.js, Python, databases), connecting the front-end and back-end, version control, and basic DevOps practices. By the end of this guide, you’ll have a clear understanding of the steps involved in becoming a full-stack developer and a solid foundation to start building your own applications.
Understanding Front-End Development
HTML, CSS, and JavaScript Fundamentals
Front-end development is the cornerstone of any web application, focusing on the user interface and user experience. Mastering HTML, CSS, and JavaScript is crucial for any aspiring full-stack developer. HTML offers the structure of the web page, CSS handles the styling and visual presentation, and JavaScript adds interactivity and dynamic behavior. Without a solid understanding of these three technologies, building complex web applications becomes significantly more challenging.
HTML (HyperText Markup Language) is the foundation of all web pages. It uses tags to define elements such as headings, paragraphs, images, and links. Understanding semantic HTML is essential for creating accessible and search engine optimization-friendly websites. For example, using
, and
tags can improve the structure and readability of your code.
CSS (Cascading Style Sheets) is used to control the visual appearance of a website. It allows you to define styles for HTML elements, such as colors, fonts, and layout. CSS frameworks like Bootstrap and Tailwind CSS can significantly speed up the development process by providing pre-built styles and components. Learning CSS preprocessors like Sass or Less can also enhance your workflow by allowing you to write more maintainable and scalable CSS.
JavaScript is a programming language that enables you to add interactivity to your web pages. It can be used to create dynamic text, handle user input, and communicate with servers. JavaScript frameworks and libraries like React, Angular, and Vue.js offer powerful tools for building complex user interfaces. Understanding the fundamentals of JavaScript, including variables, functions, and DOM manipulation, is essential before diving into these frameworks.
Popular Front-End Frameworks: React, Angular, and Vue.js
Once you have a solid understanding of HTML, CSS, and JavaScript, the next step is to learn a front-end framework. React, Angular, and Vue.js are the most popular choices, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. These frameworks offer a structured way to build complex user interfaces and manage application state.
React is a JavaScript library developed by Facebook for building user interfaces. It uses a component-based architecture, which allows you to break down complex UIs into smaller, reusable components. React also uses a virtual DOM, which improves performance by minimizing direct manipulation of the actual DOM. React is known for its flexibility and large community, making it a great choice for beginners.
Angular is a TypeScript-based framework developed by Google. It offers a thorough set of tools and attributes for building large-scale applications. Angular uses a modular architecture, which makes it easy to organize and maintain your code. Angular also has strong support for testing and dependency injection, which can improve the quality and reliability of your applications.
Vue.js is a progressive JavaScript framework that is easy to learn and use. It is known for its simplicity and flexibility, making it a great choice for small to medium-sized projects. Vue.js also has a large and active community, which offers plenty of resources and support for developers.
Choosing the right front-end framework depends on your specific needs and preferences. React is a good choice if you want flexibility and a large community. Angular is a good choice if you need a thorough framework for building large-scale applications. Vue.js is a good choice if you want a simple and easy-to-learn framework.
Responsive Design and UI/UX Principles
In today’s mobile-first world, responsive design is essential for creating websites that look and function well on all devices. Responsive design involves using CSS techniques like media queries and flexible layouts to adapt the layout of a website to varied screen sizes. Understanding UI/UX principles is also crucial for creating user-friendly and engaging websites.
Responsive Design ensures that your website looks good on desktops, tablets, and smartphones. This is achieved through fluid grids, flexible images, and media queries in CSS. Frameworks like Bootstrap and Tailwind CSS offer responsive grid systems and components that simplify the process of creating responsive layouts.
UI (User Interface) design focuses on the visual elements of a website, such as colors, typography, and layout. A good UI design should be visually appealing and easy to navigate. UX (User Experience) design focuses on the overall experience of using a website, including usability, accessibility, and performance. A good UX design should be intuitive and efficient, allowing users to accomplish their objectives quickly and easily.
Understanding UI/UX principles involves learning about user study, information architecture, and interaction design. Tools like Figma and Adobe XD can help you create wireframes and prototypes to test your designs before you start coding-basics">coding-languages">coding-projects">coding-tools">coding. By focusing on both UI and UX, you can create websites that are not only visually appealing but also offer a great user experience.
Diving into Back-End Development
Choosing a Back-End Language: Node.js, Python, Java, and More
Back-end development involves building the server-side logic and databases that power web applications. Choosing the right back-end language is a critical decision that can impact the performance, scalability, and maintainability of your application. Node.js, Python, and Java are among the most popular choices, each with its own strengths and weaknesses.
Node.js is a JavaScript runtime environment that allows you to run JavaScript on the server. It is based on the V8 JavaScript engine, which is also used by Google Chrome. Node.js is known for its non-blocking, event-driven architecture, which makes it highly efficient for handling concurrent requests. Node.js is a great choice for building real-time applications, such as chat applications and online games.
Python is a versatile programming language that is widely used in web development, data science, and machine learning. It has a simple and easy-to-learn syntax, which makes it a great choice for beginners. Python frameworks like Django and Flask offer powerful tools for building web applications. Python is also known for its large and active community, which offers plenty of resources and support for developers.
Java is a robust and scalable programming language that is widely used in enterprise applications. It is known for its platform independence, which allows you to run Java applications on any operating system. Java frameworks like Spring and Hibernate offer powerful tools for building web applications. Java is a good choice for building large-scale applications that require high performance and reliability.
Working with Databases: SQL and NoSQL
Databases are essential for storing and managing data in web applications. Understanding the varied types of databases and how to work with them is crucial for any back-end developer. SQL and NoSQL are the two main types of databases, each with its own strengths and weaknesses.
SQL (Structured Query Language) databases are relational databases that store data in tables with rows and columns. SQL databases use a schema to define the structure of the data, which ensures data integrity and consistency. MySQL, PostgreSQL, and Microsoft SQL Server are among the most popular SQL databases. SQL databases are a good choice for applications that require complex data relationships and transactions.
NoSQL (Not Only SQL) databases are non-relational databases that store data in various formats, such as JSON documents, key-value pairs, and graphs. NoSQL databases are more flexible than SQL databases and can handle large volumes of unstructured data. MongoDB, Cassandra, and Redis are among the most popular NoSQL databases. NoSQL databases are a good choice for applications that require high scalability and flexibility.
API Development and RESTful Services
APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) are essential for enabling communication between varied software systems. Understanding how to design and build APIs is crucial for any back-end developer. RESTful services are a popular architectural style for building APIs that use HTTP methods to access and manipulate resources.
API Development involves designing and building interfaces that allow varied applications to communicate with each other. REST (Representational State Transfer) is an architectural style that uses HTTP methods like GET, POST, PUT, and DELETE to manage resources. Building RESTful APIs involves defining endpoints, handling requests, and returning responses in a standardized format like JSON.
RESTful Services are designed to be stateless, meaning that each request from a client to a server must contain all the information needed to understand and process the request. This makes RESTful services highly scalable and easy to maintain. Tools like Postman and Insomnia are commonly used to test and debug APIs.
Connecting Front-End and Back-End
Understanding HTTP and the Request-Response Cycle
Connecting the front-end and back-end involves understanding how web browsers communicate with servers using the HTTP protocol. The request-response cycle is the foundation of web communication, where a client sends a request to a server, and the server sends back a response.
HTTP (HyperText Transfer Protocol) is the foundation of data communication on the web. It defines how messages are formatted and transmitted between clients and servers. Understanding HTTP methods (GET, POST, PUT, DELETE), status codes (200 OK, 404 Not Found, 500 Internal Server Error), and headers is crucial for building web applications.
The Request-Response Cycle starts when a user interacts with a web page, triggering a request from the browser to the server. The server processes the request and sends back a response, which the browser then renders to the user. This cycle is fundamental to how web applications work, and understanding it is essential for building efficient and reliable applications.
Working with APIs: Fetch and Axios
To connect the front-end and back-end, you need to use APIs to send requests and receive data. Fetch and Axios are two popular JavaScript libraries for making HTTP requests.
Fetch is a built-in JavaScript API that offers a simple and modern way to make HTTP requests. It uses Promises to handle asynchronous operations, making it easy to work with data from APIs. Fetch is supported by most modern browsers, making it a reliable choice for making HTTP requests.
Axios is a popular JavaScript library that offers a more attribute-rich API for making HTTP requests. It supports attributes like automatic JSON transformation, request cancellation, and interceptors. Axios is also compatible with older browsers, making it a good choice for projects that need to support a wide scope of browsers.
Handling Data: JSON and Data Transformation
Data is typically exchanged between the front-end and back-end in JSON (JavaScript Object Notation) format. Understanding how to parse and transform JSON data is essential for building web applications.
JSON (JavaScript Object Notation) is a lightweight data-interchange format that is easy to read and write. It is based on a subset of the JavaScript programming language and is widely used for transmitting data between servers and web applications. Understanding how to serialize and deserialize JSON data is crucial for working with APIs.
Data Transformation involves converting data from one format to another. This is often necessary when working with APIs that return data in a varied format than what the front-end expects. JavaScript offers built-in methods for parsing and manipulating JSON data, making it easy to transform data as needed.
Version Control and Collaboration
Introduction to Git and GitHub
Version control is essential for managing changes to your code and collaborating with other developers. Git is the most popular version control system, and GitHub is a web-based platform for hosting Git repositories.
Git is a distributed version control system that allows you to track changes to your code over time. It enables you to revert to previous versions, compare changes, and collaborate with other developers. Understanding Git commands like commit, push, pull, and merge is crucial for managing your code effectively.
GitHub is a web-based platform for hosting Git repositories. It offers a collaborative environment for developers to share code, track issues, and review changes. GitHub is widely used in the open-source community and is an essential tool for any developer.
Branching Strategies and Pull Requests
Branching strategies and pull requests are essential for collaborating on code projects. Branching allows you to work on new attributes or bug fixes in isolation, while pull requests offer a mechanism for reviewing and merging changes.
Branching Strategies involve creating separate branches for varied attributes or bug fixes. This allows you to work on multiple changes in parallel without interfering with each other. Common branching strategies include Gitflow and GitHub Flow.
Pull Requests are a mechanism for proposing changes to a codebase. When you are ready to merge your changes into the main branch, you create a pull request. This allows other developers to review your changes and offer feedback before they are merged.
Collaboration Tools: Slack, Jira, and Trello
Collaboration tools are essential for coordinating work and communicating with other developers. Slack, Jira, and Trello are among the most popular collaboration tools.
Slack is a messaging app that is widely used in the software industry. It offers channels for varied teams and projects, allowing developers to communicate and share information in real-time.
Jira is a project management tool that is used to track issues, plan sprints, and manage workflows. It offers a centralized platform for managing all facets of a software project.
Trello is a visual project management tool that uses boards, lists, and cards to organize tasks. It is a simple and intuitive tool that is easy to use and can be customized to fit varied workflows.
Deployment and DevOps Basics
Understanding Deployment Pipelines
Deployment is the process of making your application available to users. Understanding deployment pipelines is essential for automating the deployment process and ensuring that your application is deployed reliably.
Deployment Pipelines are automated workflows that take your code from development to production. They typically involve steps like building the application, running tests, and deploying the application to a server. Tools like Jenkins, Travis CI, and CircleCI can be used to automate deployment pipelines.
Introduction to Cloud Platforms: AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud
Cloud platforms offer a scalable and reliable infrastructure for hosting web applications. AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud are among the most popular cloud platforms.
AWS (Amazon Web Services) is a thorough cloud platform that offers a wide scope of services, including compute, storage, and database services. AWS is widely used by businesses of all sizes and is a popular choice for hosting web applications.
Azure is a cloud platform developed by Microsoft that offers a wide scope of services, including compute, storage, and database services. Azure is tightly integrated with Microsoft technologies and is a popular choice for businesses that use Microsoft products.
Google Cloud is a cloud platform developed by Google that offers a wide scope of services, including compute, storage, and database services. Google Cloud is known for its innovative technologies and is a popular choice for businesses that need to scale their applications quickly.
Basic DevOps Practices: CI/CD and Automation
DevOps is a set of practices that aim to automate and improve the software development lifecycle. CI/CD (Continuous Integration/Continuous Deployment) and automation are among the most crucial DevOps practices.
CI/CD (Continuous Integration/Continuous Deployment) is a set of practices that aim to automate the process of building, testing, and deploying software. CI involves automatically building and testing code changes whenever they are committed to a repository. CD involves automatically deploying code changes to a production environment.
Automation involves using tools and scripts to automate repetitive tasks. This can include tasks like building the application, running tests, and deploying the application to a server. Automation can improve the efficiency and reliability of the software development lifecycle.
Becoming a full-stack developer is a challenging but rewarding journey. This roadmap offers a solid foundation for beginners, covering essential technologies and skills. Remember to stay consistent, practice regularly, and never stop learning. The path to becoming a proficient full-stack developer requires dedication and continuous effort. Start building your projects today and take the next step in your career! Explore online resources, join developer communities, and continue to refine your skills. With the right approach, you can achieve your objectives and excel in the world of full-stack development. Embrace the challenge, and you’ll be well on your way to a achievementful career as a full-stack developer. Consider enrolling in a bootcamp or online course to accelerate your learning and gain practical experience. Your journey to becoming a full-stack developer starts now!