beginners">web development roadmap for beginners">
beginners">web development roadmap for beginners">
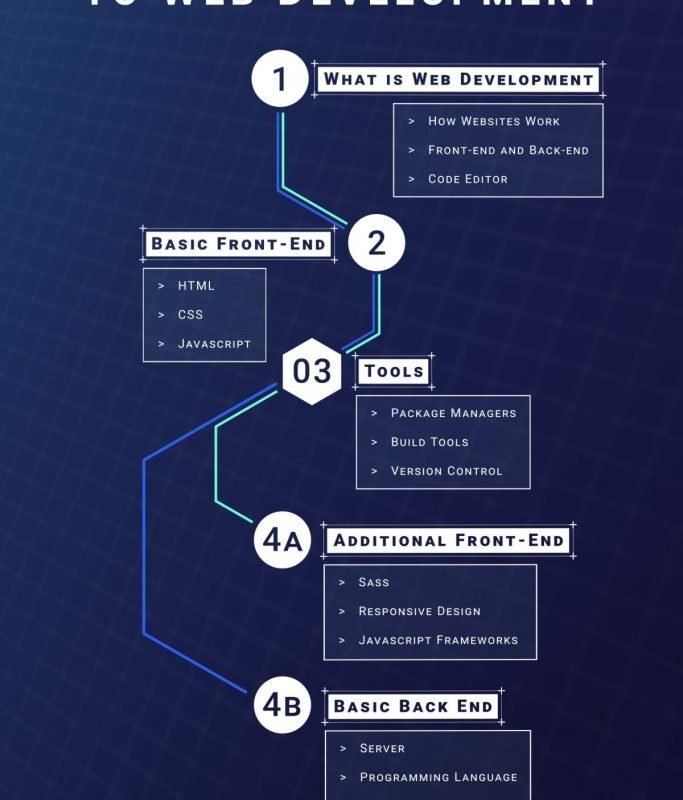
Embarking on a web development roadmap can seem daunting for beginners , but with a structured approach , anyone can learn to build amazing websites and applications. Web development encompasses a wide scope of skills and technologies , from front-end design to back-end programming. Many aspiring developers feel lost , unsure where to start or which technologies to focus on. This article offers a thorough web development roadmap for beginners , outlining the essential steps and technologies you need to learn to become a proficient web developer. We’ll cover everything from HTML , CSS , and JavaScript fundamentals to advanced frameworks , backend technologies , and databases. By following this roadmap , you’ll gain a clear understanding of the web development landscape and be well-equipped to start your journey. This article will guide you through the following key areas: HTML , CSS , and JavaScript fundamentals , front-end frameworks (React , Angular , Vue.js) , backend technologies (Node.js , Python , PHP) , databases (SQL and NoSQL) , and version control (Git and GitHub).
HTML , CSS , and JavaScript Fundamentals
HTML: Structuring the Web
HTML (HyperText Markup Language) is the backbone of any website. It offers the structure and text of web pages. Think of it as the skeleton upon which everything else is built. Without HTML , there would be no text , images , or links. Learning HTML involves understanding various tags and elements that define varied parts of a webpage. For example , the
tag is used for paragraphs ,
to
tags are used for headings , and ![]()
To get started with HTML , you should focus on the following:
- Basic HTML Structure: Understanding the
,, andtags. - Text Formatting: Using tags like
,,, andto format text. - Lists: Creating ordered (
- Links: Creating hyperlinks using the
tag. - Images: Embedding images using the
- Tables: Creating tables using the
,
, , and tags. - Forms: Building forms using the
,0 Comments - Forms: Building forms using the